Filter by price
Filter by Brand
- Lidocaine (3)
Frequently Asked Questions
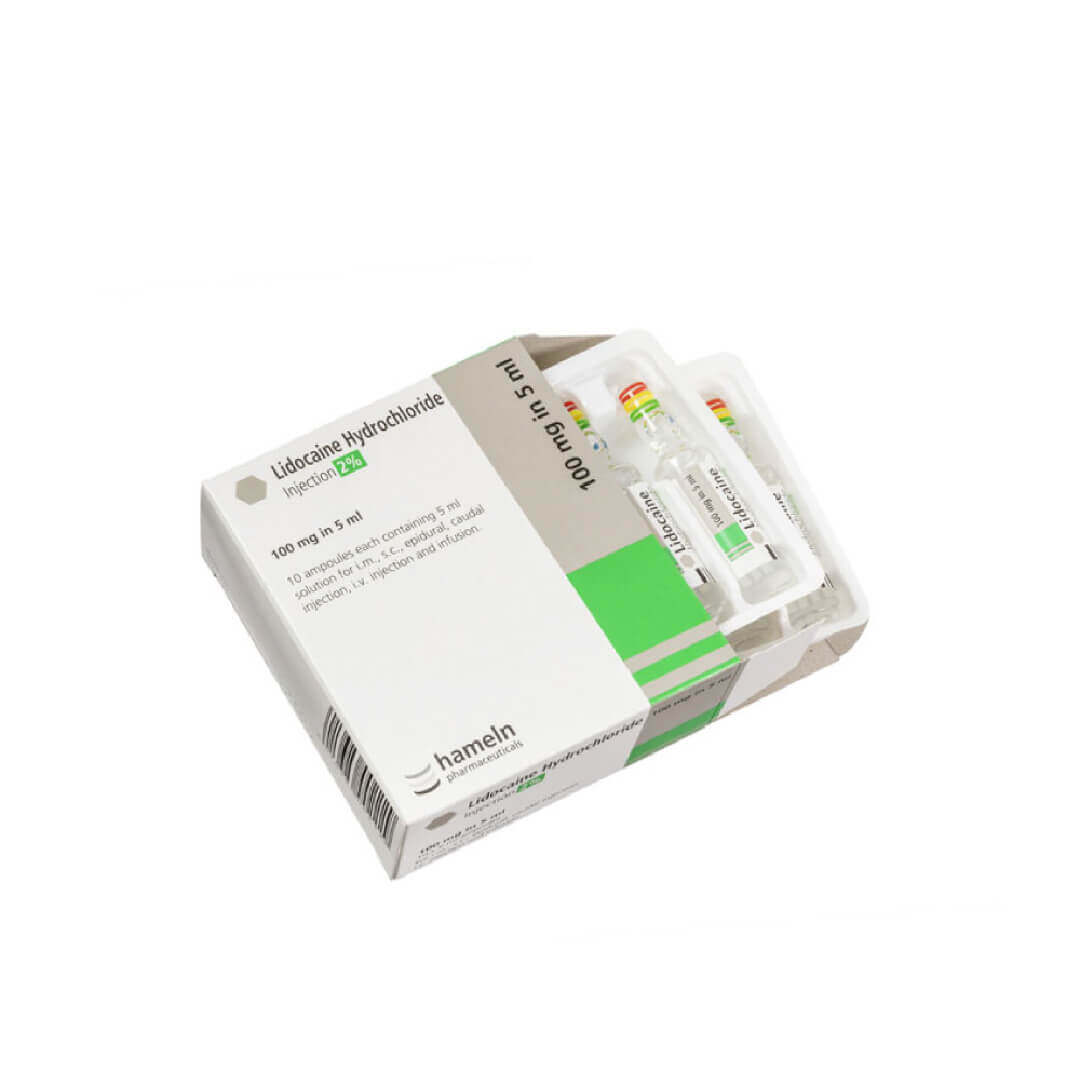
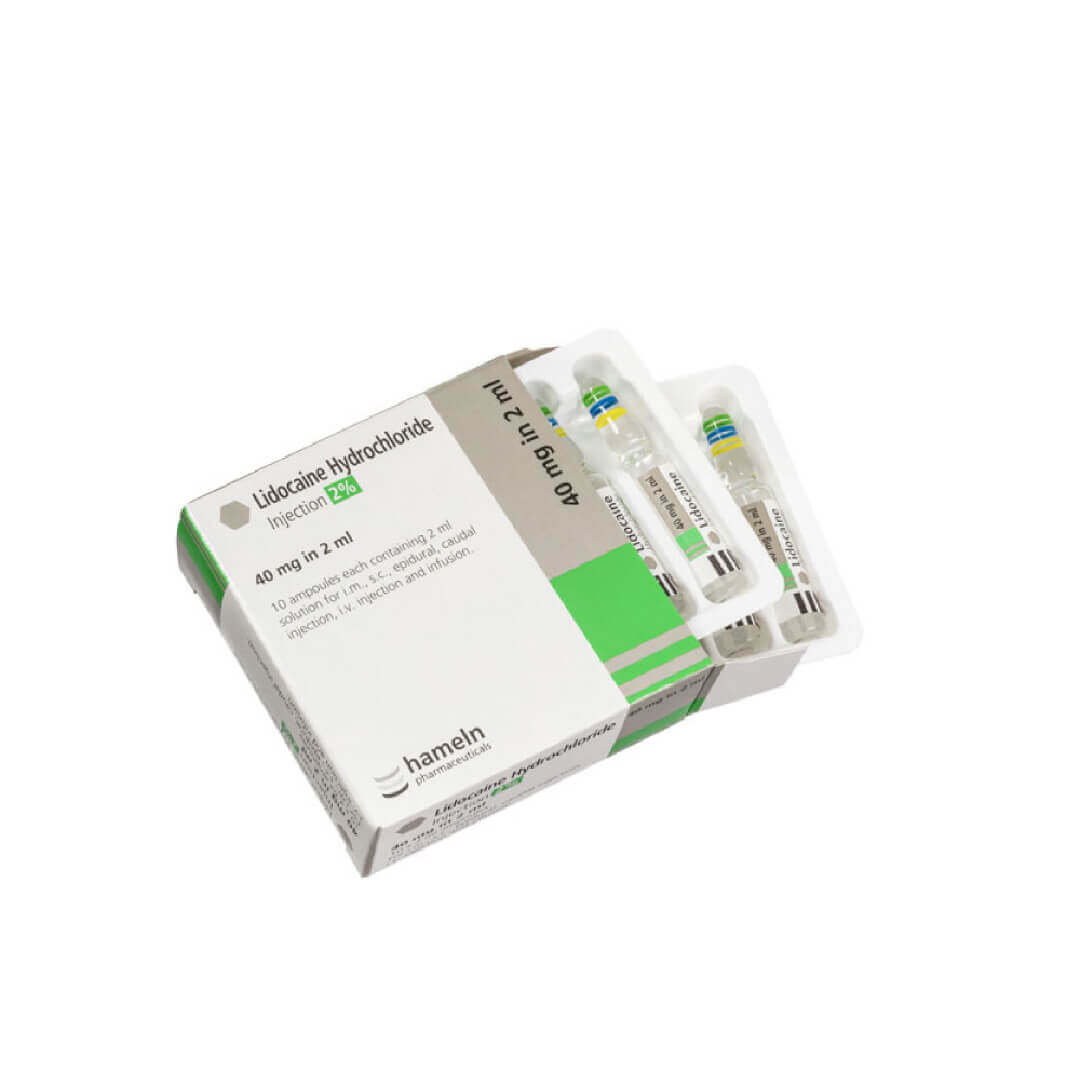
Lidocaine is a common local anesthetic used for aesthetic procedures to numb the treatment area, making sure that the patient is comfortable during invasive procedures such as injectable fillers, laser treatments, and other dermatological procedures.
There are several concentrations of Lidocaine available, the most common being 1%, 2% and sometimes 5% for topical and injectable uses in aesthetic treatments. The concentration depends on the procedure, the area being treated and the duration of analgesia required.
Yes, Lidocaine should be cautiously used for patients who have a history of cardiac conditions, liver disease, or allergies to local anesthetics. It is also suggested that patients who are pregnant or breastfeeding should not have Lidocaine, unless deemed absolutely necessary.
Lidocaine should be stored in a cool, dry place away from light. The storage temperature should be between 5°C and 30°C (59°F and 86°F). Once opened, the vials should be used promptly, any unused vials should be disposed of.
Lidocaine toxicity can cause confusion, seizures, respiratory depression, and cardiac disturbances. If toxicity is suspected, Lidocaine administration should be stopped immediately, and emergency medical services should be contacted.
The dosage depends on the patient’s weight, but typically should not exceed 4.5 mg/kg of Lidocaine without epinephrine and 7mg/kg with epinephrine. You should always calculate the total dose based on all concurrent Lidocaine-containing products used in the treatment.
Lidocaine can be mixed with other substances such as saline, or mixed with other anesthetics to enhance its effect or to prolong its duration of action. However, the mixture needs to be prepared under strict aseptic conditions and used immediately to prevent contamination.
Aesthetics professionals must ensure they are compliant with local guidelines, including proper documentation, dosing, and disposal procedures.
Practitioners should ensure proper patient assessment, consent, and accurate dosing. It is also essential to monitor patients for adverse reactions during and after the procedure. Having emergency equipment and drugs readily available is crucial in case of an adverse reaction.
If an allergic reaction occurs, discontinue the use of Lidocaine immediately. Administer appropriate emergency care including antihistamines or corticosteroids, and if necessary, epinephrine. Always have an emergency protocol in place and ensure all staff are trained on how to handle such situations.